Optimal Path Routing using Reinforcement Learning
Introduction:
Traditional routing algorithms such as Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, and Ford-Fulkerson are widely used to determine the best route from a source node to a destination node in a network. While effective, these algorithms have limitations, including complexity, processing time, and a lack of dynamism in considering real-time network conditions like traffic congestion and queue sizes. In modern network environments, where internet congestion control is critical, there is a need to dynamically modulate data transmission rates to make efficient use of network capacity. Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising solution by training deep network policies that can adapt to changing network conditions, improving routing performance and efficiency.
Objective:
To develop an AI-based routing system that utilizes reinforcement learning to dynamically optimize network traffic flow. The goal is to overcome the limitations of traditional routing algorithms by creating an environment that can adjust to real-time network conditions, leading to more efficient and effective routing decisions.
Environment:
An environment was created using OpenAI Gym to simulate and test the learning agents responsible for controlling network traffic.
States: The state vector comprises three elements that describe the network’s current condition: Latency Gradient: The derivative of latency with respect to time. Latency Ratio: The ratio of the current monitor interval’s (MI) mean latency to the minimum observed mean latency. Sending Ratio: The ratio of packets sent to packets acknowledged by the receiver. The state at any time T is represented as {v t−k+d ,…,v t−d}, where k is the window time, and d represents the delay.
Actions: The actions involve changes to the sending rate (at) by the transmitter, which can adjust its transmission rate at the start of each monitor interval (MI).
Rewards: The reward function is defined as:
Reward = 10×Throughput−1000×Latency−2000×Loss This function balances throughput, latency, and loss to optimize network performance.
Algorithm:
Two key reinforcement learning algorithms were employed in this project:
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO): PPO is a reinforcement learning algorithm that optimizes a neural network policy to maximize expected rewards. It uses a surrogate objective function to prevent large policy updates that could destabilize learning or degrade performance.
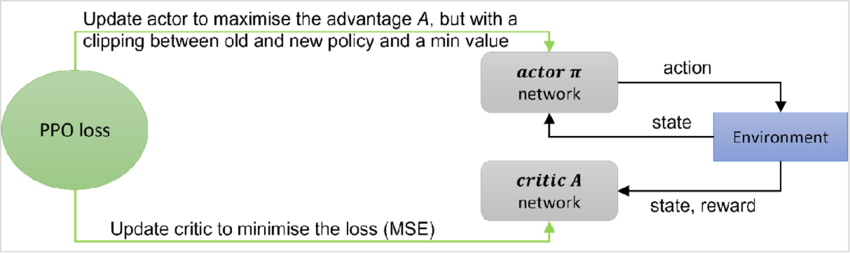
Example application: training an agent to play complex games like Atari’s Breakout.
- Hindsight Experience Replay (HER):HER enhances learning efficiency by allowing the agent to learn from failed experiences. It relabels unsuccessful experiences as successful by altering the agent’s goal to the achieved state rather than the originally desired state.
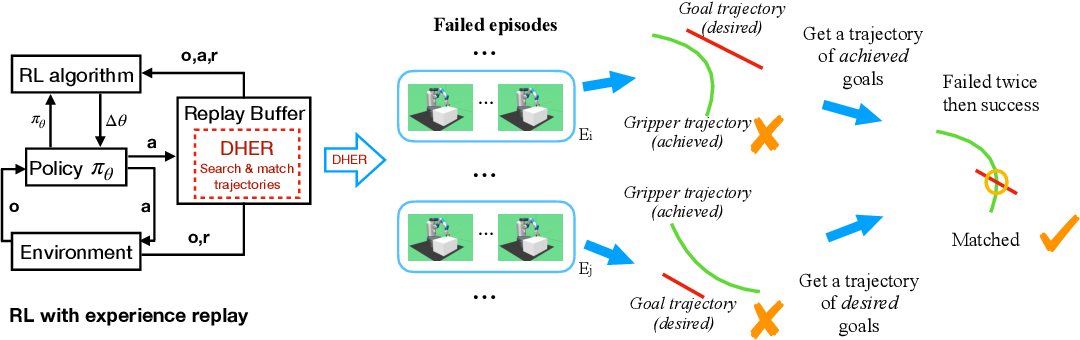 Example application: training an agent to solve robotic tasks like stacking blocks.
Example application: training an agent to solve robotic tasks like stacking blocks.
Deliverables:
- AI-Based Routing System: A reinforcement learning-based system capable of dynamically adjusting network traffic flow.
- Simulation Environment: An OpenAI Gym-based environment for testing and refining the AI model.
- Optimized Neural Network Policy: A neural network policy optimized through PPO and HER, capable of making real-time routing decisions.
- Read more here
Conclusion:
The Optimal Path Routing project demonstrates the potential of reinforcement learning in revolutionizing network traffic control. By moving beyond traditional algorithms and embracing dynamic, AI-driven solutions, this project contributes to more efficient and responsive network management. The integration of reinforcement learning algorithms like PPO and HER in routing can lead to significant improvements in network performance, paving the way for smarter, more adaptive networks
